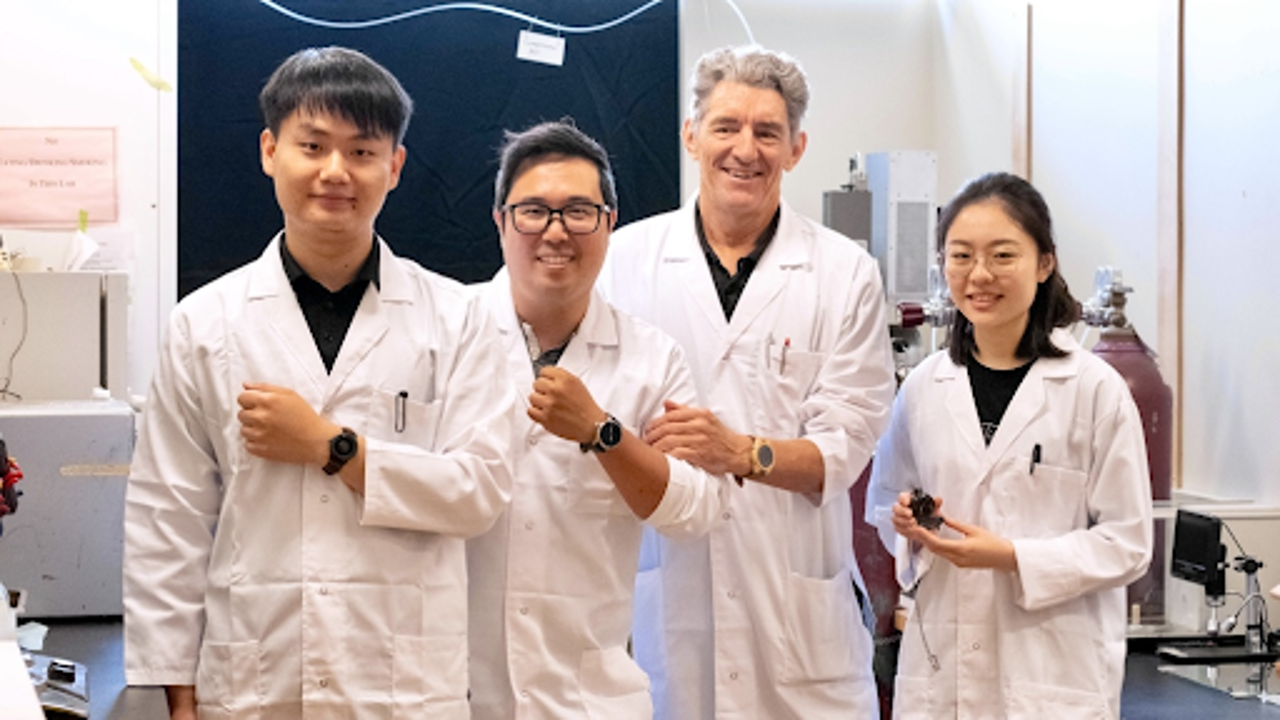
UBC forestry researchers Dengcheng Feng, Kenny Cheng, Philip Evans, and Sara Xu are pictured from left to right. CTV News
Researchers at the University of British Columbia (UBC) have made an exciting breakthrough with a new material that is exceptionally good at absorbing light. This "super-black" material, which absorbs almost all visible light, was discovered unexpectedly while working on a project to make wood more water-resistant.
Forestry professor Philip Evans and his PhD student Kenny Cheng were experimenting with a technique called high-energy plasma etching, which they were using to create a surface texture on wood that repels water, similar to the lotus leaf. During their experiments, they found that when they applied this technique to the end grain of the wood, it turned an extremely dark shade.
Intrigued by the results, they decided to send a sample to Texas A&M University for further analysis. The experts at Texas A&M confirmed that the material absorbed 99.3% of visible light, which is well above the threshold for what is classified as "super-black" or "ultra-black" materials. For comparison, regular black paint absorbs about 97.5% of light.
Researchers said that super-black materials could be very useful in astronomy because they help cut down on stray light and make telescope images clearer. CTV News
The UBC team has named their discovery Nxylon, combining "Nyx," the Greek goddess of night, and "xylon," the Greek word for wood. Unlike other super-black materials, such as Vantablack, which are made from carbon nanotubes, Nxylon is derived from basswood, a common and renewable resource in North America. This makes it an environmentally friendly alternative to other super-black materials that have raised environmental concerns.
Super-black materials have a variety of uses. They are valuable in astronomy, where they help reduce stray light and enhance the clarity of telescopic images. They are also used to create more efficient solar panels and luxury items like watches and jewelry, which can replace expensive gemstones or rare woods.
The researchers created sample watches and jewelry with the new super-black wood. CTV News
The UBC researchers have already started experimenting with Nxylon in prototype watches and are exploring other potential uses. They are in the process of launching a startup, Nxylon Corporation of Canada, to bring their discovery to market. Possible applications for Nxylon include car dashboards, theatre wall cladding, and interior panels for aircraft.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Nxylon is that it retains its deep black colour even when covered with a gold coating for scientific analysis. This is because the colour is due to the material's structure rather than pigments or dyes.
Evans, who has worked on combating illegal logging, sees Nxylon as a potential substitute for endangered dark woods like ebony and rosewood. By providing a viable alternative, Nxylon could help reduce the demand for these precious timbers and combat illegal logging practices.