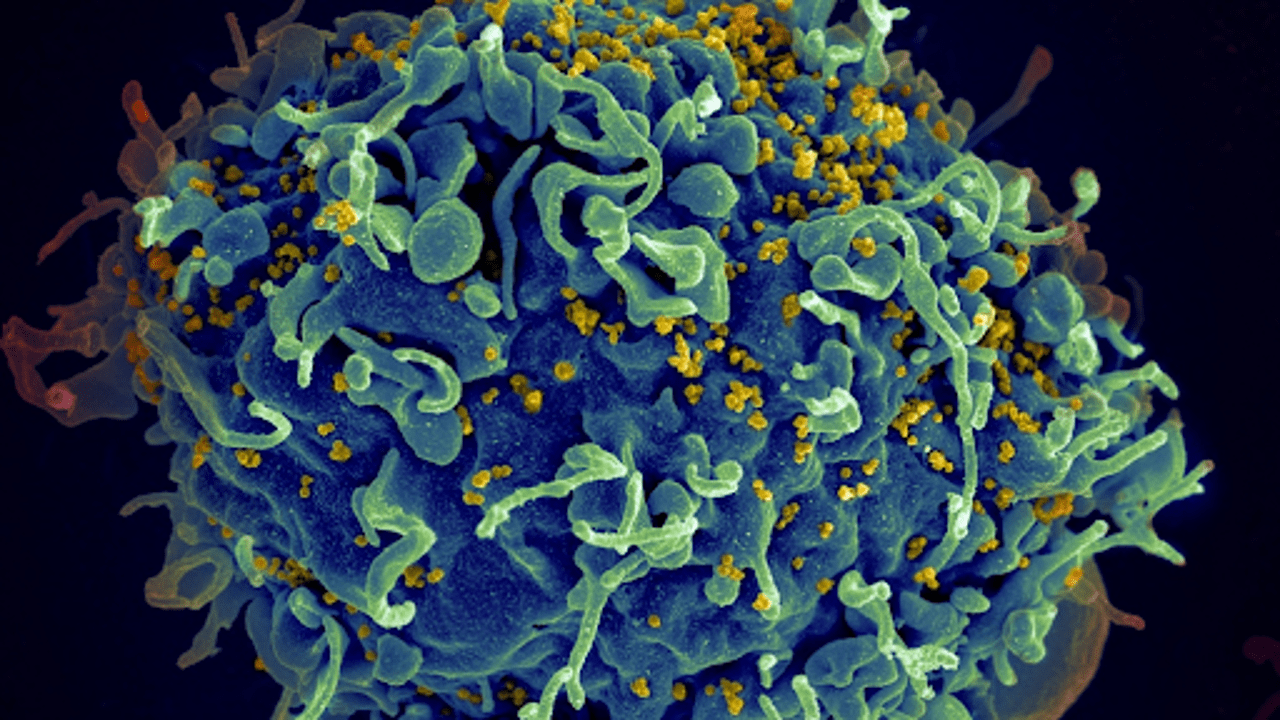
An image captured by an electron microscope, provided by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, reveals a human T cell, shown in blue, being attacked by HIV, depicted in yellow. HIV is the virus responsible for causing AIDS. AP Photo
Researchers in Montreal have made a significant breakthrough in the fight against HIV by finding a potential way to eliminate the virus from its hiding spots within the body. These hidden areas, known as HIV reservoirs, have long been a major obstacle in eradicating the disease. According to Professor Eric Cohen, whose team at the Montréal Clinical Research Institute (IRCM) made this discovery, targeting and removing these reservoirs is key to curing HIV and ultimately ending the need for lifelong medication.
While HIV is no longer considered a fatal disease, thanks to antiretroviral drugs, it remains a chronic condition. These medications allow people with HIV to live normal lives as long as they continue taking their treatment. However, if someone stops taking their medication, the virus can emerge from its dormant state and cause the disease to return with full force. In addition to this challenge, the presence of HIV reservoirs has been linked to chronic inflammation, which can lead to other health issues such as cognitive problems, heart disease, and certain cancers.
The virus hides in cells that are resistant to destruction, making it difficult for researchers to not only locate the virus but also eliminate it. Over the years, scientists have worked hard to uncover where the virus resides and develop strategies to rid the body of it for good.
Recent progress in HIV research has been inspired by a small number of cases in which people with HIV appeared to recover spontaneously after receiving stem cell transplants for cancer. This suggests that HIV can be cured, but the key to this lies in finding ways to clear the virus reservoirs.
Professor Cohen's lab began exploring the potential of a family of molecules called ²SMAC Mimetic (SM)², which are typically used to treat cancer. Their approach involved reactivating dormant HIV and then targeting the reactivated cells for destruction through a process known as apoptosis, or cell death. Cohen's team partnered with Ascentage Pharma to test one specific molecule, APG-1387, which is currently undergoing clinical trials for cancer treatment. In their laboratory tests, APG-1387 was successful in reducing the size of HIV reservoirs in mice that had been infected and treated with retroviral drugs.
Furthermore, when the mice stopped taking their antiretroviral treatment, the virus rebounded more slowly, suggesting that the APG-1387 treatment was effective in reducing the latent reservoirs of HIV. This strategy, known as "shock and kill," aims to reactivate the virus so that the immune system can recognize and eliminate the infected cells. The molecules used in the experiment not only reawaken the virus but also make the infected cells more vulnerable to destruction.
While the results of the study are promising, Cohen noted that the reduction in HIV reservoirs is not yet enough to fully eradicate the disease. If treatment stops, the virus can still return. Future work will focus on combining this approach with immune system-stimulating interventions to further reduce the virus reservoirs and bring researchers closer to the goal of curing HIV.