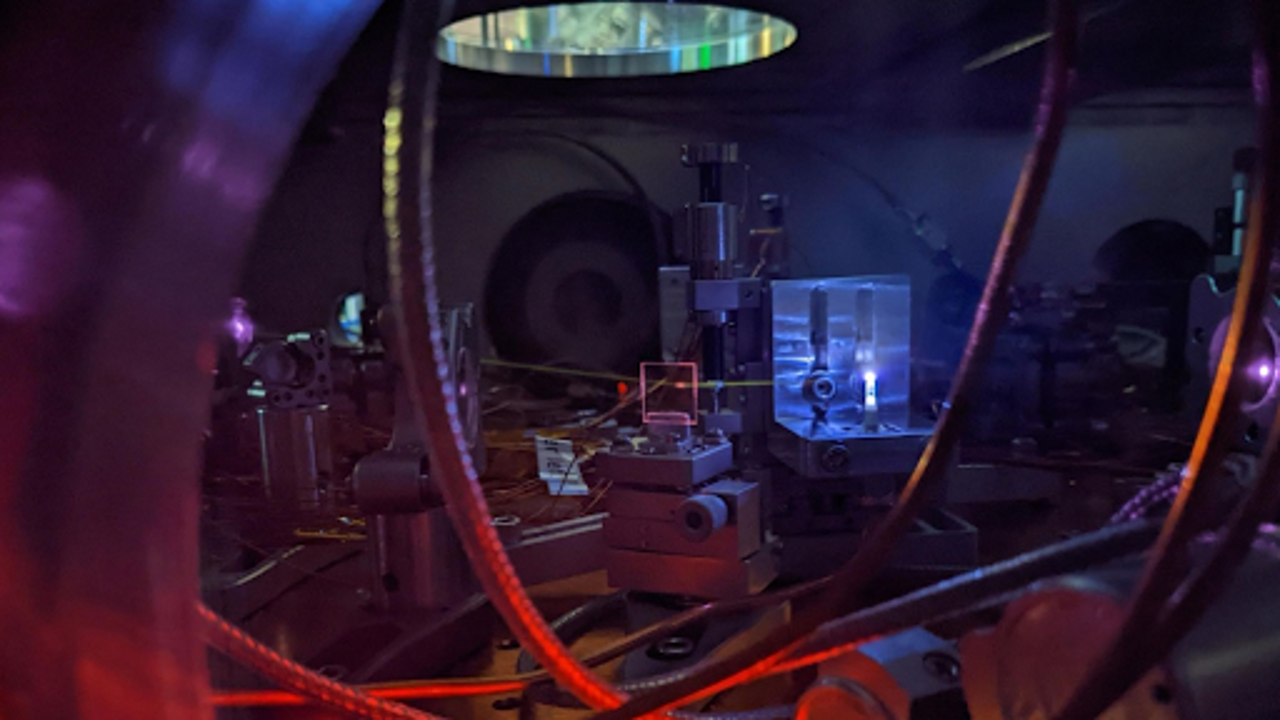
In a recent study, scientists used UV light to activate nuclear particles within a thorium-229 atom to create a nuclear clock. CNN
Imagine a clock so precise that it can run for a billion years without losing even a second. Scientists have now taken significant steps towards achieving such incredible accuracy. This potential breakthrough involves nuclear clocks, which are expected to far surpass even the best atomic clocks we use today.
Atomic clocks, which measure time-based on the vibrations of electrons within atoms, are currently the most accurate tools we have for timekeeping. They work by using signals that excite atoms, causing their electrons to jump between energy levels billions of times per second. These oscillations mark the passage of time.
However, a new method could make timekeeping even more accurate. Scientists have developed a way to excite particles in the nucleus of an atom using ultraviolet light, targeting the thorium-229 isotope. This process is more complex than atomic clocks, as triggering energy jumps in the nucleus requires a much higher frequency signal. The result could be a clock that is even more precise than atomic clocks, which are vulnerable to electromagnetic disturbances.
The experiment, conducted using a solid crystal embedded with thorium-229, involved measuring the frequency of energy pulses affecting the nucleus. This process was made possible through an advanced tool called an optical frequency comb, which counts the waves of ultraviolet light interacting with the nucleus. Although the prototype isn’t as accurate as atomic clocks yet, it’s a promising step forward.
“There are many ways to improve the accuracy,” said study coauthor Chuankun Zhang from JILA, a joint research center at the University of Colorado Boulder. Zhang added that tweaks to the lasers’ alignment and frequency could further enhance precision. This advancement marks "the dawn of a nuclear clock," according to Dr. Olga Kocharovskaya, a physicist from Texas A&M University.
Previously, atomic clocks have been essential for technologies like GPS, space exploration, and maintaining international time standards. However, atomic clocks can be disrupted by electromagnetic interference. In contrast, nuclear clocks, which measure time by focusing on the tightly bound particles in an atom's nucleus, would be much more stable.
Efforts to develop nuclear clocks have been ongoing since the 1970s when it was discovered that the thorium nucleus could be excited using vacuum ultraviolet light. Recent progress has made tracking the signals produced during nuclear transitions easier, with the new thorium-229 results being about a million times more precise than previous attempts.
While nuclear clocks are not yet fully developed, scientists believe they could revolutionize timekeeping. These clocks could also provide new insights into fundamental physics by allowing researchers to compare time measurements from nuclear and atomic clocks. This comparison could help determine whether the basic constants of physics, like dark matter, are as unchanging as we believe.
Though there is still work to be done, researchers are optimistic about the future of nuclear clocks. As technology improves and the mysteries of nuclear clocks are better understood, this innovative timekeeping method could unlock new possibilities in physics and beyond.