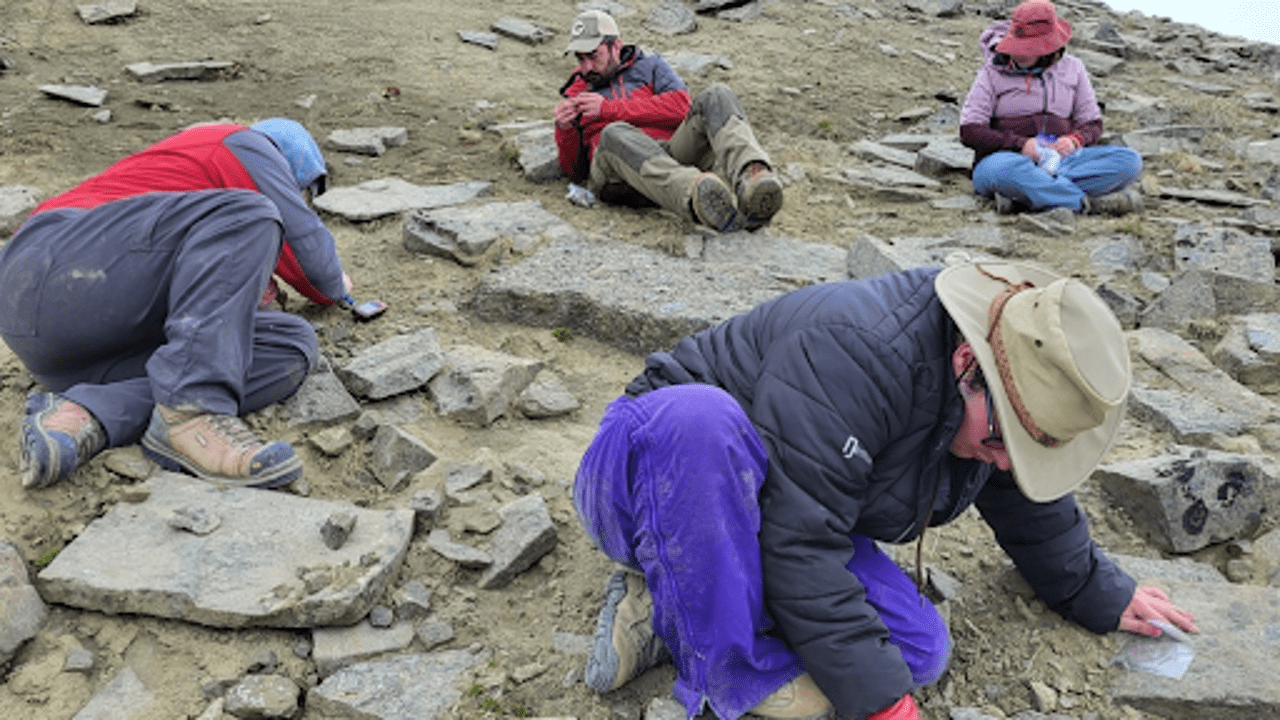
Paleontologists search for fossils in the Sustut Basin of northern B.C. Royal B.C. Museum
Paleontologists from the Royal B.C. Museum have made an exciting discovery in the northern mountains of British Columbia. High in the Spatsizi Plateau Wilderness Provincial Park, about 2,000 meters above sea level, they have uncovered a remarkable collection of fossils. This area, located roughly 500 kilometres north of Smithers in the Skeena Mountains, is typically reached by float plane or helicopter due to its remote location.
Over the past three years, researchers have been working in this challenging terrain, using helicopters to access the fossil site. They have uncovered a diverse range of well-preserved dinosaur remains. The discovery includes more than 90 fossils, featuring teeth from relatives of the Tyrannosaurus rex and Triceratops, as well as bones from a large herbivore and the foot of a small carnivorous dinosaur.
These fossils date back about 66 to 68 million years, originating from a region known as the Sustut Basin. Previously, only one dinosaur species from this area, Ferrisaurus sustutensis, had been identified. Victoria Arbour, the project's lead researcher and curator of paleontology at the museum, called the site "unlike any other in Canada."
Arbour explained why this discovery is so significant. Typically, dinosaur fossils are found in places where sediment accumulates, such as riverbeds and coastal areas, which help preserve the remains. Finding fossils on a mountain is unusual because the rocky, sandy conditions are not ideal for fossilization. During the late Cretaceous Period, when these dinosaurs lived, the mountains in what is now northern B.C. were even taller, making this discovery particularly intriguing.
The fossils' location suggests that dinosaurs lived in varied environments, and this find could help fill in gaps in our understanding of prehistoric ecosystems. Arbour noted that because the site is so unique, there is a good chance that some of the discovered species may be new to science.
Lead researcher Victoria Arbour displays fragments of a tyrannosaur tooth. Royal B.C. Museum
The process of analyzing these fossils will involve careful extraction from the surrounding rock and transportation to the museum's new PARC Campus in Colwood, B.C. This campus will serve as a secure facility for the museum’s collections and research. The public will have a chance to view the research process through special viewing windows at the campus.
Arbour expressed excitement about the potential new discoveries, especially a set of small bones from the foot and leg of a small predator. These bones could belong to a raptor-like dinosaur, which would be a rare find. If the fossils turn out to be from known species like T. rex or Triceratops, it could suggest these dinosaurs were capable of surviving in environments different from their usual habitats.
Royal B.C. Museum CEO Tracey Drake called the discovery "remarkable," highlighting its significance in revealing new aspects of the province’s history. She expressed eagerness to share the insights gained from this research with the public.
This research has received support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, BC Parks, and the Trebek Initiative, a collaboration dedicated to protecting and preserving Canada's natural and cultural heritage, named in honor of the late Alex Trebek.