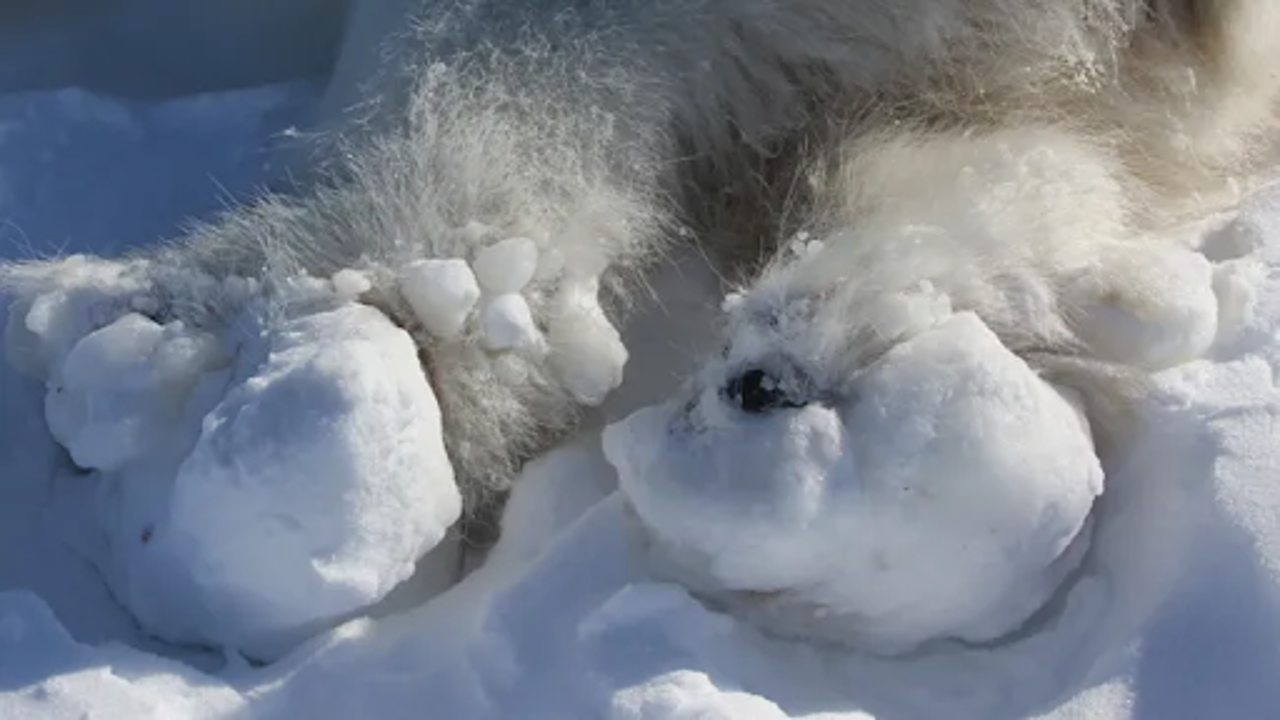
The image depicts the back feet of a polar bear that was briefly sedated for research in East Greenland in 2022. The bear had significant ice formations stuck to its paws, which the researchers took off. Live Science
Polar bears are suffering serious injuries on their paws due to changing ice conditions in the Arctic, according to a recent study. Researchers have documented alarming cases of ice balls forming on the feet of some bears, leaving them with painful, bleeding wounds.
In the most extreme instances, two bears were found with large ice masses, comparable in size to dinner plates, attached to their paws. These ice balls prevented them from walking or running effectively. "I'd never seen that before," said Kristin Laidre, a marine ecologist and the lead author of the study from the University of Washington. "The two most affected bears couldn't run — they couldn't even walk very easily."
This marks the first time such injuries have been reported in polar bears. The study was published on October 22 in the journal Ecology. The ice balls likely form when slushy snow gets trapped in the pads of the bears' feet, which normally provide traction on icy surfaces. As this snow accumulates, it freezes into solid blocks measuring about 12 inches across, causing significant pain.
"The chunks of ice weren't just caught up in the hair," Laidre explained. "They were sealed to the skin, and when you palpated the feet it was apparent that the bears were in pain."
Researchers examined two populations of polar bears in northern Greenland and found that roughly one in four bears had ice-related injuries. Most affected were adult males, known for travelling longer distances and weighing more than females and cubs. Between 2012 and 2022, Laidre and co-author Stephen Atkinson, a wildlife biologist and veterinarian, studied these bears as part of population assessments.
In the Kane Basin population, 31 out of 61 bears showed signs of laceration, skin ulceration, or ice buildup on their paws. Alarmingly, in 2012 and 2013, 73% of adult males in this area were affected. In the East Greenland population, from 2018 to 2022, 15 out of 124 bears exhibited similar injuries.
Researchers believe the wounds may stem from rising Arctic temperatures, which contribute to wetter snow and freeze-thaw cycles. This creates fragile ice surfaces that can injure the bears' paws. Additionally, increased rainfall in the Arctic is causing snow to become slush, which can get trapped in the bears' feet and freeze, exacerbating the problem. The melting and refreezing of surface snow creates a hard crust that heavy bears can break, leading to further injuries.
Indigenous hunters in Kane Basin were aware of these injuries and associated them with increased activity during mating and hunting seasons. However, they also recognized these injuries as a new issue. The hunters have noticed similar problems with their sled dogs, leading them to trim the fur between their dogs' pads to prevent ice buildup.
John Whiteman, an assistant professor of biology at Old Dominion University and a chief research scientist at Polar Bears International, commented on the surprising nature of these findings. "This report is definitely surprising," he said. "If the conditions that encourage ice clumps become a common occurrence across a large area, more bears would be at risk for foot damage."
As climate change continues to impact the Arctic environment, the health and survival of polar bears face new challenges. The evidence of these injuries highlights the urgent need for further research and understanding of how changing conditions affect these iconic animals.