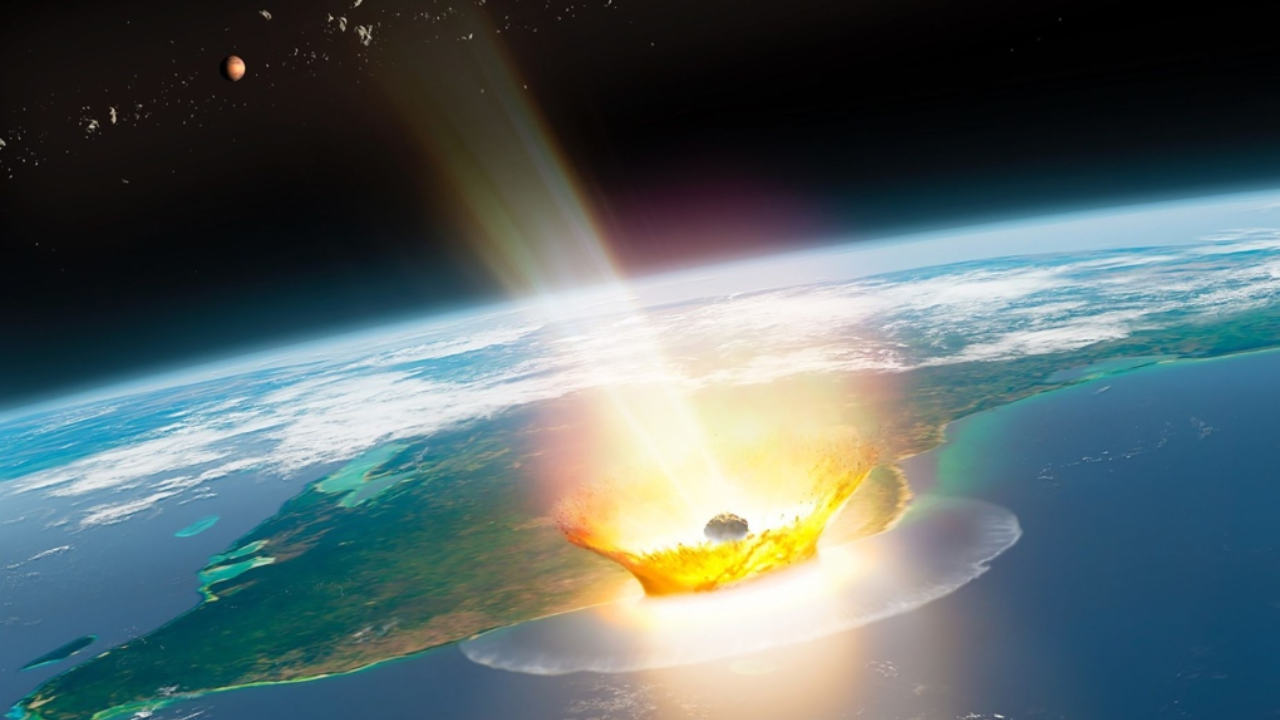
A study identified the chemicals of the asteroid that hit the Yucatán Peninsula in Chicxulub, Mexico, 66 million years ago, causing the extinction of most dinosaurs. (CNN Newsource)
Sixty-six million years ago, Earth experienced a catastrophic event when an asteroid struck the Yucatán Peninsula, where Chicxulub, Mexico, is today. This collision led to the extinction of about 75% of all animal species, including most dinosaurs except birds. Surprisingly, little remains of the asteroid itself, but a new study published in the journal Science has revealed crucial details about its chemical composition.
Researchers have discovered that the asteroid was a rare clay-rich mudball containing materials dating back to the dawn of the solar system. This revelation is significant as it helps us understand the dynamic nature of our solar system, according to Dr. Steven Goderis, a coauthor of the study and a research professor of chemistry.
Back in 1980, scientists hypothesized that a giant space rock collision caused the dinosaurs' extinction. They found a thin layer of iridium, a metal rare on Earth but abundant in some asteroids, in 66-million-year-old rocks worldwide. This led to skepticism among some scientists. However, in 1991, the discovery of the Chicxulub crater, dated to the same period, provided strong evidence supporting the asteroid collision theory.
The asteroid responsible for this mass extinction was enormous, likely between 6 and 9 miles in diameter. Traveling at a staggering speed of 15.5 miles per second, it generated immense kinetic energy upon impact, converting it into heat. Dr. Goderis explained that this impact vaporized the asteroid, creating a global dust cloud that blocked sunlight and lowered temperatures, leading to mass extinction. The asteroid's chemical trace, a thin clay layer found worldwide, is all that remains.
The study, led by Dr. Mario Fischer-Gödde of the University of Cologne, examined the chemical composition of this clay layer. Researchers sampled rocks from Denmark, Italy, and Spain, isolating the metal ruthenium, which, like iridium, is more common in space rocks. By comparing this with other asteroid impact sites and meteorites, they concluded that the asteroid was likely a carbonaceous chondrite. These ancient space rocks often contain water, clay, and organic compounds.
Interestingly, while carbonaceous chondrites are common in space, only about 5% of meteorites that fall to Earth belong to this category. This finding helps us understand the asteroid's unique properties and the catastrophic event it caused.
The implications of these findings extend beyond understanding our past. While impacts of this scale are rare, occurring every 100 million to 500 million years, the possibility of another large space rock collision with Earth remains. Knowing the physical and chemical properties of such objects is crucial for developing strategies to protect ourselves from potential future impacts. Dr. Goderis emphasized the importance of missions like NASA's 2022 DART mission, which aimed to redirect an asteroid. Understanding how different types of asteroids react to physical forces is essential for effective planetary defense.
Dr. Ed Young, a professor of cosmochemistry at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the study, praised the research. He stated that the discovery adds depth to our understanding of the dinosaur extinction event and supported the conclusion that the asteroid was a carbonaceous chondrite.