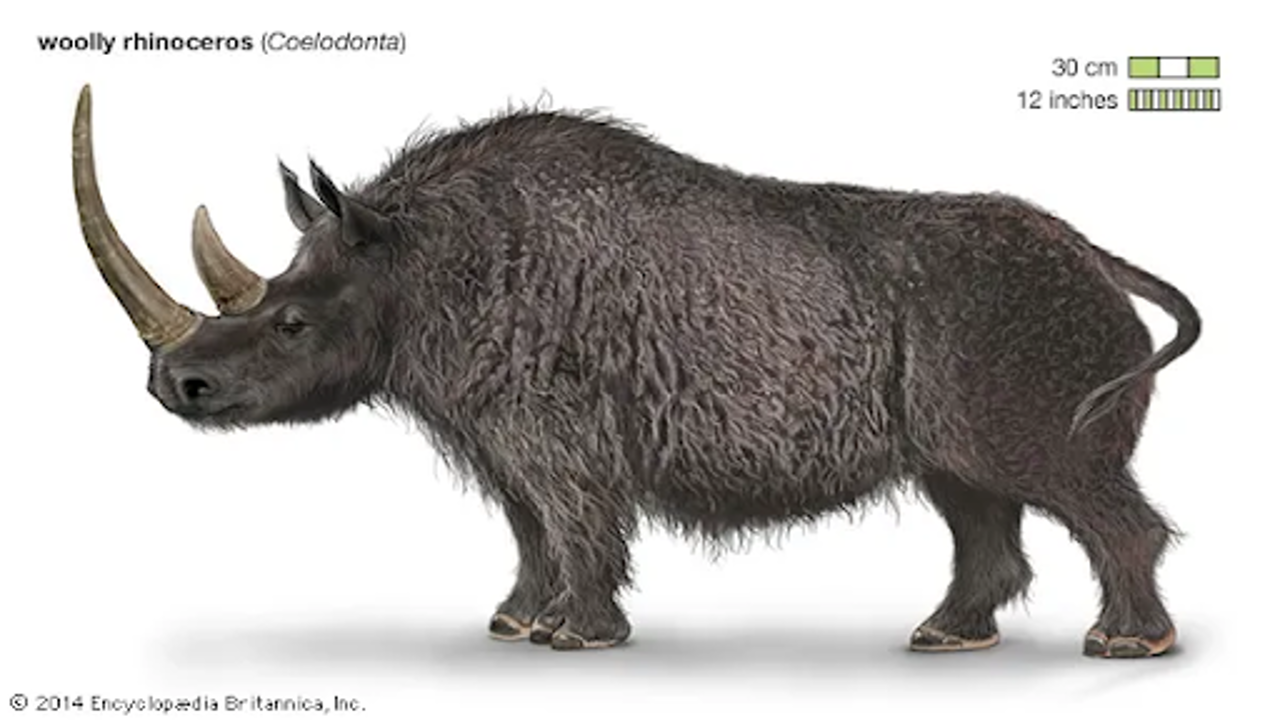
An artistic depiction of a woolly rhinoceros (Coelodonta antiquitatis). Britannica
Scientists have unearthed the mummified remains of a young woolly rhinoceros, buried for over 32,000 years in the icy Siberian tundra. This remarkable discovery offers an incredible glimpse into the distant past when these mighty creatures roamed the Arctic plains. While the right side of the rhino’s body is astonishingly well-preserved, showing patches of its original fur and skin, the left side tells a different story. It appears to have been scavenged by predators either shortly before or after the rhino’s death.
The study, published by researchers from the Russian Academy of Sciences and the Republic of Sakha, provides a detailed analysis of the carcass. The scientists noted significant damage to the left side of the rhino’s body, especially around the thigh and shoulder blade, with most of the internal organs missing. This damage points to predatory animals feasting on the young rhino. Additionally, remains of small crustaceans found in the animal’s fur suggest that it may have perished in a shallow pool of water.
Radiocarbon dating has revealed that the woolly rhino met its end over 32,000 years ago. Woolly rhinos, along with woolly mammoths, were dominant herbivores during the Ice Age, thriving in the harsh Arctic climate. These animals were well adapted to the cold, thanks to their thick fur coats, but much remains unknown about their lives and behaviours.
The discovery of this well-preserved specimen, now referred to as the "Abyisky rhinoceros" after the local district where it was found, is filling some of those gaps. The carcass was recovered in August 2020 from the banks of the Tirekhtyakh River in northeastern Russia and is currently housed in a freezer at the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Sakha. Scientists have already conducted preliminary studies, taking samples of its fur, skin, and other tissues. They also closely examined the animal’s teeth, horns, and even a curious feature – a hump on its back filled with fat.
In August 2020, scientists retrieved the remains from the ice in Russia's Sakha Republic. Live Science
This hump, which is about five inches high, has never been seen before in woolly rhinos but is common in other Arctic creatures. According to evolutionary genomics expert Love Dalén, these fatty humps evolved to help animals survive extreme conditions by storing energy. Such a finding deepens scientists’ understanding of how these prehistoric animals adapted to their environment.
The Abyisky rhino was roughly 4 to 4.5 years old when it died, based on its horn measurements and teeth analysis. Although not yet sexually mature, the rhino’s dark brown coat differed significantly from that of "Sasha," a smaller, lighter-coloured woolly rhino calf found in the same area in 2014. Adult woolly rhinos, however, typically had coarse, dark brown fur, similar to that of the Abyisky specimen.
This discovery is particularly valuable to researchers because it offers an almost complete body with preserved soft tissue. Such specimens are rare and provide crucial information for genetic studies that wouldn’t be possible with just bones. As scientists continue to study the Abyisky rhino, this ancient animal may reveal even more secrets about life during the Ice Age.