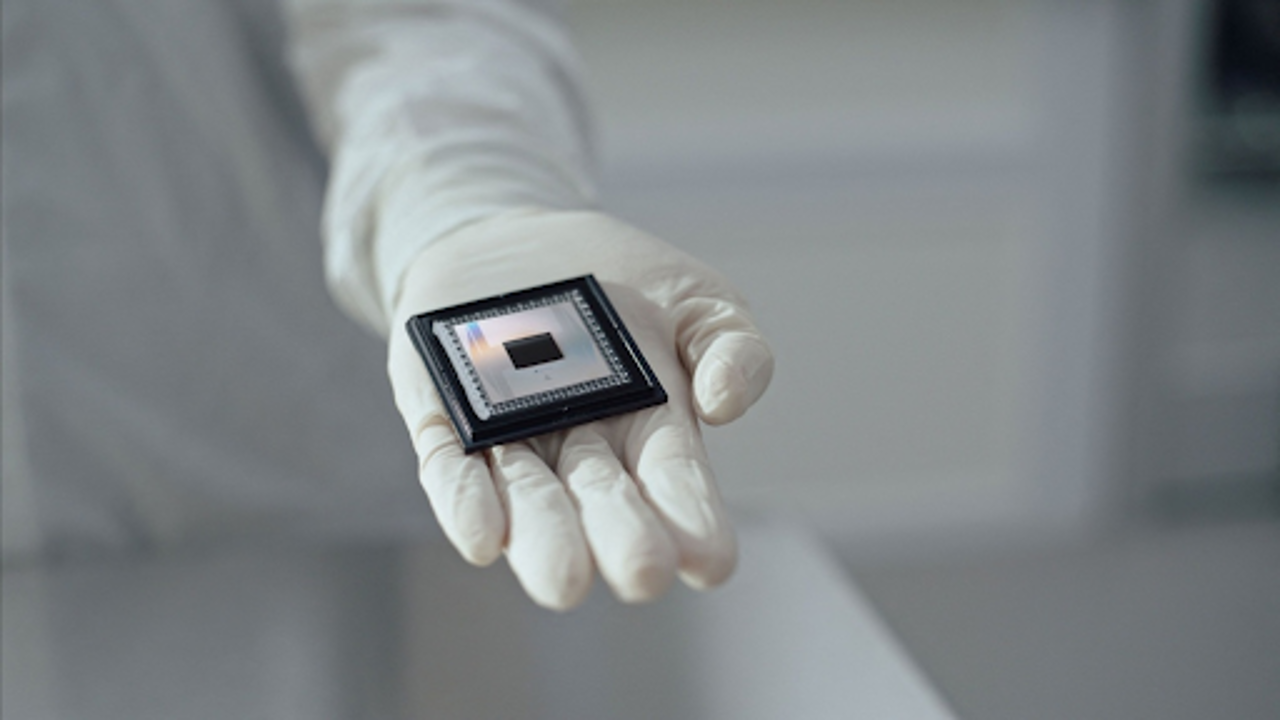
On December 6, Google Quantum AI unveiled its new "Willow" chip. Reuters
Google has made a major breakthrough in quantum computing, announcing the successful use of a new chip that solves a complex problem in just five minutes. This is a task that would take a traditional computer far longer—almost an impossible amount of time, equivalent to the history of the universe. This achievement brings Google closer to its goal of making quantum computers practical for solving problems beyond the capabilities of today's fastest systems.
Quantum computing, which is pursued by several tech giants like Microsoft and IBM, promises to vastly increase computing power and speed. Although the problem solved by Google’s new chip does not have immediate commercial applications, the company believes that quantum computing could one day revolutionize fields like medicine, battery chemistry, and artificial intelligence, which are currently out of reach for traditional computers.
The breakthrough came from a new quantum chip named Willow, which is built with 105 "qubits." These qubits are the core of quantum computers, acting as the basic units of information, similar to bits in classical computers. While qubits are incredibly fast, they are also prone to errors, which can be caused by even the smallest disruptions, such as particles from outer space.
In quantum computing, adding more qubits typically leads to more errors. This has been one of the biggest hurdles for researchers, as error rates increase as qubits are added. Since the 1990s, scientists have been trying to develop ways to correct these errors. Google’s new chip, however, has addressed this issue by connecting its qubits in such a way that error rates decrease as the number of qubits increases. This is a significant step forward and marks a key breakthrough in making quantum computers more reliable and practical for real-world applications. Moreover, Google’s chip can correct errors in real time, further improving its efficiency.
Hartmut Neven, the leader of Google’s Quantum AI unit, expressed confidence in their progress, stating, “We are past the break-even point,” which indicates that they are now moving beyond the experimental phase and into making quantum computing a viable technology.
In 2019, IBM had challenged Google's previous claims about its quantum chip, questioning whether the problem truly required the time Google suggested. However, Google has taken these criticisms into account in its latest results, acknowledging that under the most ideal conditions, a classical computer would take about a billion years to solve the same problem. This further highlights the significant leap made by Google’s quantum chip.
While other companies have made chips with a higher number of qubits, Google’s focus is on ensuring that its qubits are as reliable as possible. The company has also invested in a dedicated fabrication facility for its Willow chip, speeding up the production process for future developments. This facility will enable faster innovation and testing, as the chips need to be kept in extremely cold conditions during experiments.
Anthony Megrant, chief architect for Google Quantum AI, noted that with their new fabrication facility, the team can quickly implement ideas and accelerate their work in quantum computing. This will enable Google to continue pushing the boundaries of what quantum computers can achieve.