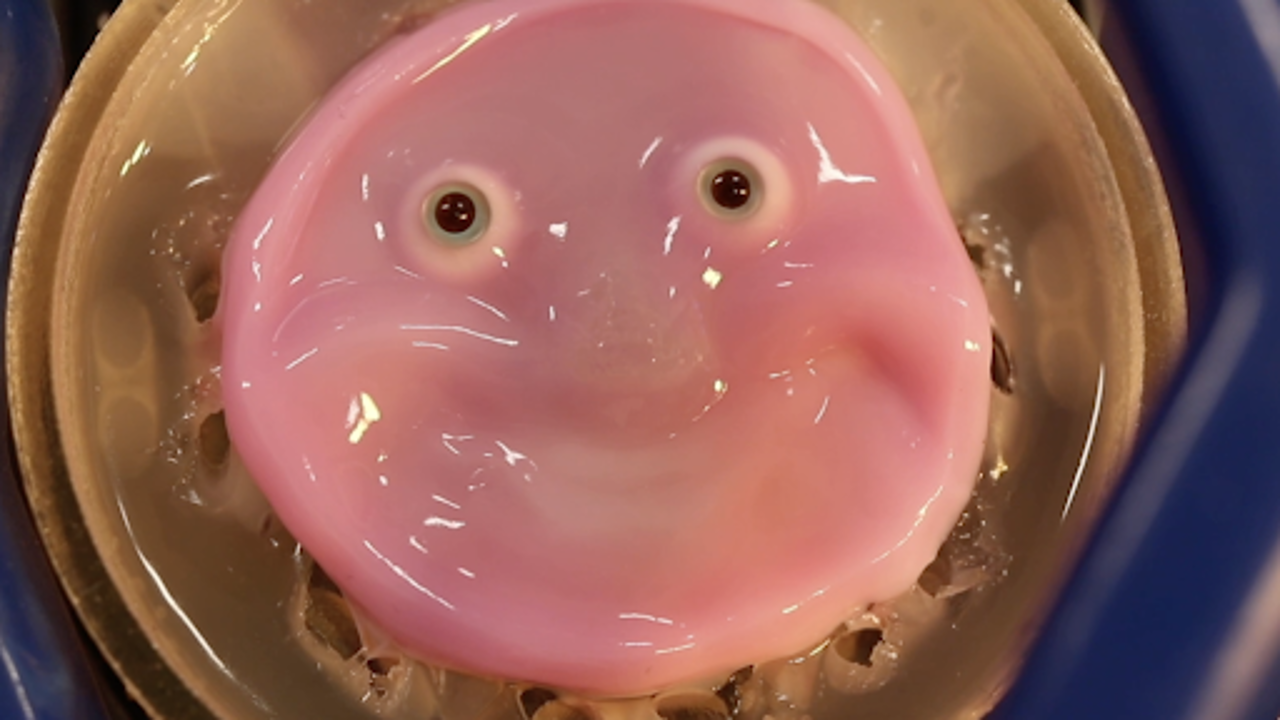
Researchers at the University of Tokyo in Japan have found an innovative method to attach skin tissue to the mechanical framework of robots.
Imagine a robot that smiles back at you with realistic, living skin. In a groundbreaking development from Japan, researchers have successfully integrated living skin tissue onto a mechanical surface, potentially transforming the way robots interact with humans.
Led by Professor Shoji Takeuchi at the University of Tokyo’s Institute of Industrial Science, the team achieved this feat using collagen and human dermal fibroblasts, mimicking the fibrous protein and cells found in human skin. Unlike previous methods that often resulted in skin detachment or breakage, the new technique involves anchoring the living skin tissue with collagen gel into V-shaped holes on the robot’s surface, ensuring a seamless and durable attachment.
The quest to make robots more human-like isn’t new. Robots like Ameca, hailed as one of the most advanced humanoids, utilize artificial intelligence to engage in conversations and react to human responses. According to Will Jackson, CEO of Engineered Arts Ltd, which developed Ameca, realistic eyes are crucial for enhancing human-robot interactions. Eyes provide expressive capabilities, helping robots like Ameca connect emotionally with people.
Unlike industrial robots primarily used in manufacturing, humanoid robots such as Sophia and Grace from Hanson Robotics aim for roles in hospitality, healthcare, and education. These humanoids, however, often face challenges with facial expressions that fall into the "uncanny valley" — a discomforting gap between human-like appearance and behavior.
Professor Takeuchi emphasizes the importance of lifelike facial expressions in healthcare, where empathy and emotional connection play significant roles in patient care. Realistic robots could potentially revolutionize healthcare by improving communication with patients.
The recent study, detailed in Cell Reports Physical Science, marks a significant leap forward in robotics. Yifan Wang, an expert in soft robotics from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, sees the integration of living skin as bridging the gap between traditional rigid robotics and softer, more biological designs. Human skin, with its sensory abilities to perceive temperature, humidity, and textures, presents a unique challenge in robotic design, one that this research aims to address.
The potential for robots to sense and respond to environmental stimuli like humans is promising. Professor Takeuchi's team plans to enhance the skin's sensory functions in future research phases, making robots more adaptive and responsive.
However, challenges remain, particularly in maintaining the consistency and quality of the living skin over time. Takeuchi’s ongoing research explores the development of a vascular system for the robotic skin, similar to human blood vessels, to sustain its health and longevity. This innovation could significantly enhance the durability and functionality of robots in various applications.
The implications of this research extend beyond robotics, potentially influencing advancements in prosthetics and biomedical devices. By integrating biological components into mechanical systems, researchers are paving the way for a future where machines not only look human-like but also feel and interact with us in more natural and intuitive ways.