Source : The Canadian Press
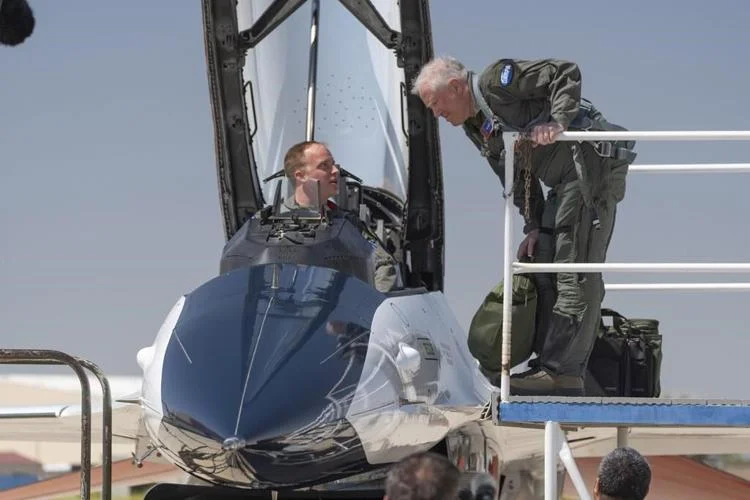
Amidst the scorching midday sun at Edwards Air Force Base in California, an experimental F-16 fighter jet, painted in striking orange and white, roared into the sky with the familiar thunderous sound characteristic of American airpower. However, what unfolded in the aerial battle that ensued was unprecedented: this particular F-16 was not piloted by a human but controlled entirely by artificial intelligence (AI). Seated in the cockpit was Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall, witnessing firsthand a historic moment in military aviation.
The integration of AI marks a significant leap forward in military aviation, rivalling the impact of stealth technology introduced in the early 1990s. The U.S. Air Force has embraced this innovation vigorously, envisioning a future fleet comprising over 1,000 unmanned AI-enabled warplanes, with the initial deployment scheduled for 2028.
The choice of Edwards Air Force Base for this groundbreaking demonstration holds historical significance. Renowned for its role as the birthplace of aerospace breakthroughs, including Chuck Yeager's breaking of the sound barrier, the base has long been a hub for classified aerospace research and development. Here, within classified simulators and highly secure facilities, a new generation of test pilots is training AI algorithms to navigate the complexities of aerial warfare.
Secretary Kendall's visit to witness AI-controlled flight firsthand underscores the Air Force's confidence in this technology's future role in combat. In an interview following the flight, Kendall emphasized the imperative of incorporating AI into military operations from a security standpoint.
The AI-controlled F-16, dubbed Vista, executed lightning-fast maneuvers, subjecting Kendall to intense gravitational forces as it engaged in simulated combat with a human-piloted counterpart. Despite concerns regarding autonomous decision-making in warfare raised by experts and humanitarian organizations, Kendall expressed trust in AI systems, affirming that human oversight will always remain integral.
The military's pivot towards AI-enabled aircraft is motivated by considerations of security, cost-effectiveness, and strategic advantage. With potential adversaries such as China making significant strides in electronic warfare and unmanned aerial systems, the U.S. seeks to maintain its competitive edge by embracing AI technology.
Vista's unique training methodology sets it apart from AI programs elsewhere, leveraging real-world flight data to refine its algorithms iteratively. While China also possesses AI capabilities, the absence of real-world testing outside simulators gives the U.S. an edge in AI-driven aerial combat development.
Despite the rapid progress in AI-controlled flight, concerns linger among pilots regarding the potential implications for their roles in future conflicts. Nonetheless, they recognize the necessity of adapting to this evolving landscape to ensure national security.
As Secretary Kendall aptly summarizes, the race to harness AI in military aviation necessitates unwavering commitment and agility in order to stay ahead of adversaries.