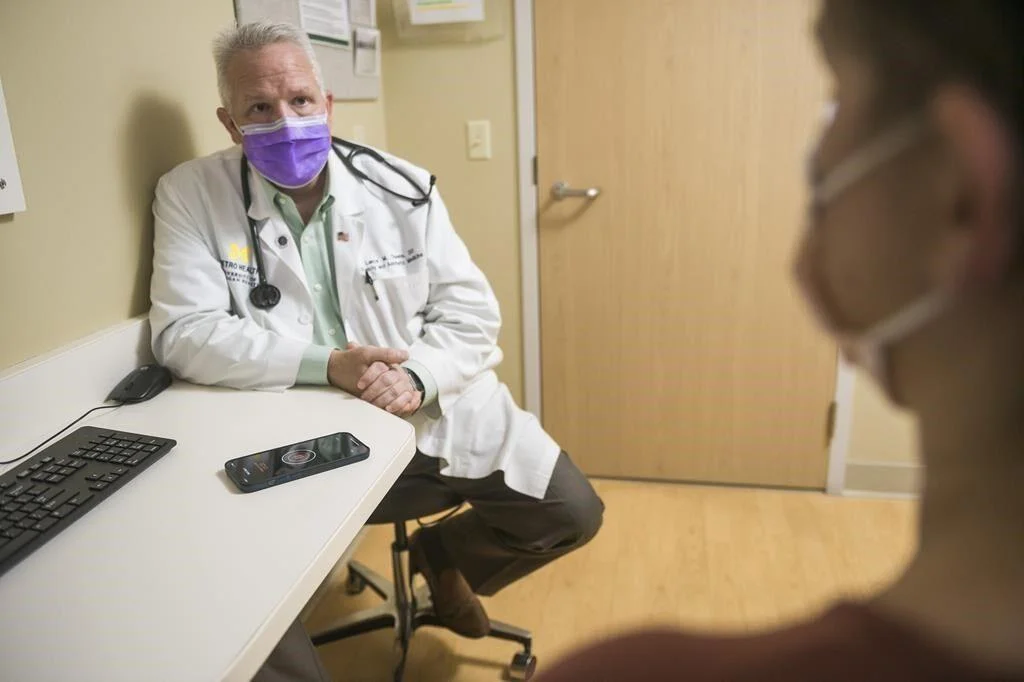
In this photo provided by University of Michigan Health-West, Dr. Lance Owens, chief medical information officer at the university, demonstrates the use of an AI tool on a smartphone in Wyoming, Mich., on Sept. 9, 2021. The software listens to a doctor-patient conversation, documents and organizes it to write a clinical note. (University of Michigan Health-West via AP)
Doctors are increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) into their practices, utilizing AI tools to streamline communication with patients and enhance efficiency. These tools, based on large language models like OpenAI's ChatGPT, are revolutionizing patient-doctor interactions and medical note-taking, offering benefits such as time-saving and burnout prevention for healthcare professionals. However, the integration of AI also raises concerns regarding trust, privacy, and the future of human connection in healthcare.
AI-driven innovations are reshaping various aspects of patient care. For instance, smartphone apps powered by AI can record and transcribe medical conversations during appointments, providing instant notes for both doctors and patients. These AI tools ensure comprehensive documentation of medical visits, potentially optimizing billing processes and enhancing patient outcomes. While patients should be informed and consent to the use of such tools, disclosure practices vary among healthcare providers and systems.
The introduction of AI into medical communication introduces complexities related to accuracy and transparency. AI-generated messages must undergo scrutiny by healthcare professionals before being sent to patients to ensure accuracy and relevance. Despite efforts to prevent inaccuracies, AI tools may still misinterpret information or fabricate responses, posing risks to patient care and electronic health records. However, healthcare providers serve as crucial safeguards, reviewing AI-generated notes for accuracy and authenticity.
Moreover, AI tools aim to emulate human empathy and friendliness in communication, enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction. However, they may occasionally produce inaccurate or alarming messages, highlighting the need for careful oversight and human intervention. While AI can facilitate certain aspects of patient-doctor communication, maintaining the human touch remains essential in delivering quality healthcare.
Privacy concerns also accompany the adoption of AI in healthcare. While healthcare systems must ensure data security and compliance with privacy regulations, the utilization of patient data to enhance AI tools raises potential risks of breaches or misuse. However, healthcare providers express confidence in the data security measures implemented by AI tool developers, emphasizing their commitment to safeguarding patient information.
Overall, the integration of AI into medical communication presents opportunities to improve efficiency and patient care. While AI tools offer benefits such as time-saving and enhanced documentation, they also raise ethical and practical considerations that must be addressed to ensure patient safety, privacy, and trust in healthcare delivery.















