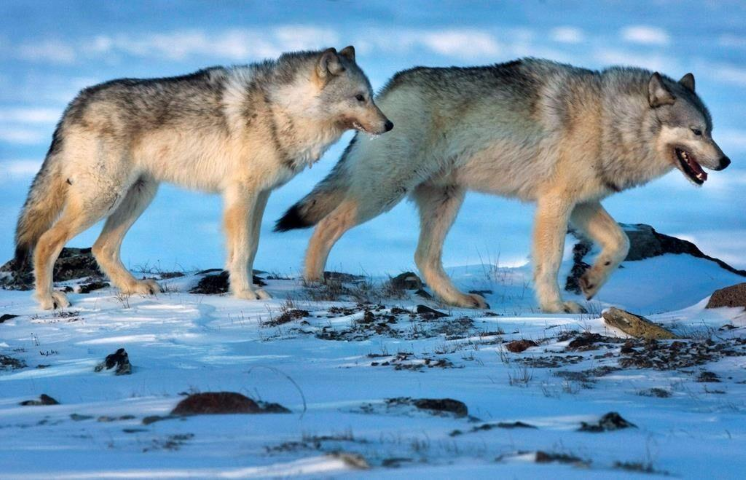
A female wolf, left, and male wolf roam the tundra near The Meadowbank Gold Mine in Nunavut on Wednesday, March 25, 2009. Health Canada says it will completely ban strychnine after completing public consultations on the use of the powerful poison. THE CANADIAN PRESS/Nathan Denette
Health Canada announced its intention to fully prohibit the use of a potent poison utilized for predator control following comprehensive public consultations regarding strychnine.
Lynn Lee from the Pest Management Regulatory Agency conveyed on Wednesday, during a conference call attended by stakeholder groups and monitored by The Canadian Press, that "All uses of strychnine are canceled." Lee cited unacceptable environmental risks associated with strychnine usage under current licensing conditions.
The forthcoming decision, set to be officially disclosed on Thursday, marks a reversal from the agency's previous proposal in 2022, which would have permitted certain applications of strychnine to persist. However, according to Lee, feedback during the subsequent 90-day comment period prompted this change.
The agency has outlined a six-month phaseout period, culminating in the complete prohibition of strychnine use by September 7. Registrations for products containing the poison will be revoked as of Thursday.
Strychnine has long been employed to manage animal pests, notably predators like coyotes and wolves. Despite its effectiveness, strychnine is widely criticized for its perceived cruelty, causing muscle cramps that eventually lead to the animal's suffocation—a method described by a veterinary professor as "one of the worst ways to die."
The rationale behind the regulatory agency's reversal remains undisclosed pending further details expected on Thursday.
Environmental organizations have consistently highlighted the broader ecological threats posed by strychnine-laden carcasses to various wildlife species beyond the intended targets.
The Alberta government, a prominent user of strychnine against wolves encroaching into caribou habitats, is among the affected parties. Alberta's strychnine program, operational from 2005 to 2018, resulted in the deaths of numerous animals, including wolves, foxes, coyotes, and eagles. Alberta discontinued strychnine use in 2020, opting for helicopter gunning as an alternative method.
Animal welfare groups, including Humane Canada and the Humane Society International, have consistently opposed strychnine.
While welcoming the decision, Sadie Parr of We Howl, an animal and conservation advocacy group, emphasized ongoing opposition to compound 1080, another predator-control substance. Health Canada plans to maintain registrations for compound 1080 while implementing enhanced measures to safeguard non-target species and improve user protective gear.
Parr underscored that the campaign against compound 1080 persists despite this development.