Small particles connected to deaths in Toronto. Toronto Star
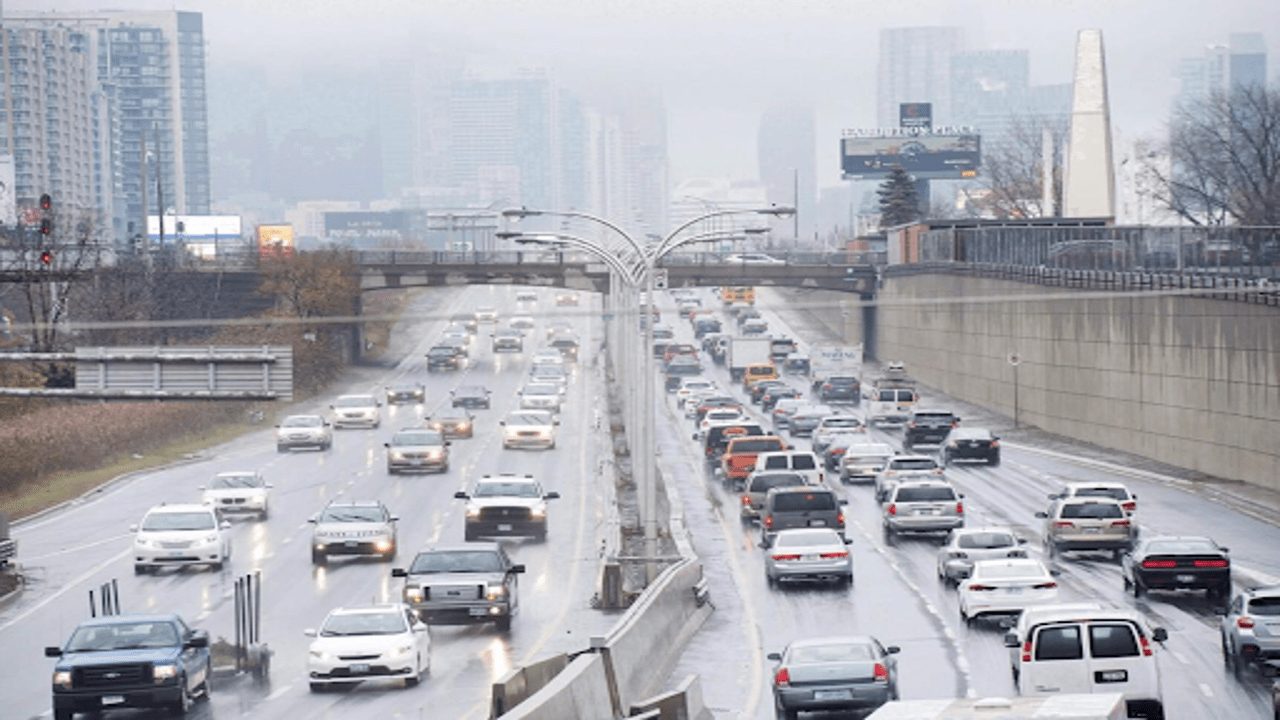
A recent study by researchers at McGill University reveals that a tiny air pollutant linked to vehicle and industrial emissions contributes to an estimated 1,100 deaths annually in Canada’s largest cities, Toronto and Montreal.
Published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the study highlights the dangers of ultrafine particles (UFPs), which are smaller than 100 nanometers. These minuscule particles are known to significantly impact health. The researchers examined air pollution levels from 2001 to 2016 and analyzed data from about 1.5 million people to understand how exposure to UFPs affects mortality rates.
Scott Weichenthal, the study’s lead investigator and an assistant professor at McGill’s Department of Epidemiology, Biostatistics, and Occupational Health, explained that long-term exposure to UFPs is linked to higher mortality rates. This is particularly true for those living near major sources of pollution, such as highways, airports, and rail yards. The particles can penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream, increasing the risk of heart and lung diseases, as well as some cancers.
The study found that areas in Toronto and Montreal with high traffic or industrial activity have elevated levels of UFPs. In Montreal, for example, the eastern part of the city, with its heavier industrial presence, shows higher concentrations compared to the western side.
Despite these findings, Weichenthal noted that regulations for UFPs are lacking. Unlike larger particles, such as soot from wood burning, which are already regulated, UFPs currently have no specific concentration limits. Weichenthal calls for more attention to be given to these particles, suggesting that new policies and monitoring systems be introduced to address their emissions.
The study underscores the need for regulatory changes to manage the health risks associated with UFPs. By targeting pollution sources and implementing stricter air quality standards, it’s hoped that future health impacts can be mitigated.